There’s so many translation terms and tools to learn, it can seem like you’re having a conversation in another language.
For easy reference, here are translation terms for beginners that will help when you’re researching translation services or beginning to work with a translation or localization services professional.
Scroll down to see the full list of definitions.
Translation Terms for Beginners
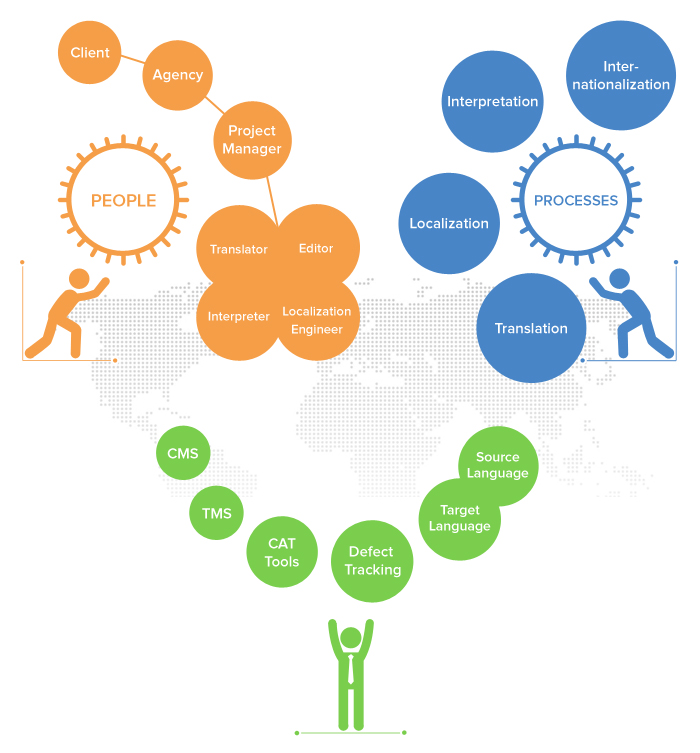
The People
Client – A company needing translation or localization services. They hire an agency or a team of independent freelance linguists to adapt their products or content for foreign markets.
Agency – A language service provider that manages whole localization and translation projects on behalf of clients by contracting or employing linguists.
The Linguists
Project Manager – Working for the agency, project managers coordinate all activities for localization and translation.
Translator – A person with professional skills in translating one language to another.
Editor – A person with professional skills in translation who provides editing for translated text.
Interpreter – A person with professional skills in facilitating communication from one language to another in real time.
Localization Engineer – They isolate files to be translated, put it back together again after translation, and make the necessary adjustment to make your content appear to be tailor-made for any market. This might be done for:
- websites and e-commerce
- video
- Elearning
- other pieces of software
Localization engineers also assist with internationalization of a product.
Localization QA Tester – Tests localized products to make sure they are ready to go to market.
The Processes
Translation – The process of translating words and writing from one language (the source language) into another (the target language). The cost is based on balancing time and quality.
Interpretation – The real-time facilitation of communication between users of different languages, either oral or signed.
Localization – The process of adapting a product or service to a particular language and culture.
Internationalization – Preparing a website, software, or an app for localization. Take a look here to find more on the difference between localization and internationalization.
Tools
Source language – The language to be translated from.
Target language – The language to be translated to.
Translation Management System (TMS) – A type of software that manages the project information, process workflow, and language assets required for large-scale translation activity. A TMS is used by agencies and linguists.
Content Management System (CMS) – A content management system allows publishing, editing, and modifying content as well as maintenance from a central interface. Most modern websites run on a CMS.
Computer-Assisted Translation (CAT) Tools – CAT tools support the translation process. This could be anything from text search tools to electronic dictionaries, to translation memory and terminology tools that manage a database of existing translated phrases.
Defect Tracking – Software that keeps track of translation and localization defects, letting project stakeholders manage and monitor the quality assurance testing process.
Localization Solutions Tailored for You
Why do 92% of multinational companies invest in localization? For starters, to become a true multi-national brand by bringing their products and services to a global audience.
Summa Linguae Technologies works with global partners with a need for practical innovation in multilingual communication. We help companies to understand each other, connect, and prosper.


